What Is Electrical Muscle Stimulation?
Electrical muscle stimulation (EMS) is a technique that uses electrical impulses to stimulate muscle contractions. This technology is used in various fields, including physical therapy, sports medicine, and fitness.
EMS involves the use of electrodes that are placed on the skin over the targeted muscles. The electrodes deliver electrical impulses that cause the muscles to contract and relax in a rhythmic pattern. The frequency and intensity of the electrical impulses can be adjusted based on the patient’s needs.
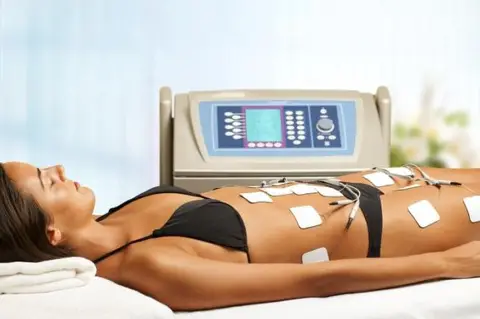
EMS can be used for a variety of purposes, including rehabilitation after injury, improving muscle strength and endurance, and pain relief. In some cases, EMS may also be used as a way to enhance athletic performance.
Rehabilitation: EMS is commonly used in physical therapy to help patients recover from injuries. For example, if a patient has a knee injury, EMS can be used to stimulate the quadriceps muscles and help them regain strength and function. EMS can also be used to reduce pain and inflammation and improve range of motion.
Muscle strength and endurance: EMS can also be used to improve muscle strength and endurance in healthy individuals. When used in combination with traditional resistance training, EMS can enhance the effects of the exercise and promote greater muscle growth and strength.
Pain relief: EMS can be used to alleviate pain in a variety of conditions, including chronic pain, fibromyalgia, and post-surgical pain. The electrical impulses stimulate the release of endorphins, which are natural painkillers produced by the body.
Athletic performance: EMS for muscle can be used to enhance athletic performance by improving muscle strength, endurance, and power. In sports medicine, EMS is often used to help athletes recover from injuries and return to play faster.
There are various types of EMS devices available, including transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation (TENS) units, neuromuscular electrical stimulation (NMES) units, and interferential current (IFC) devices. TENS units are typically used for pain relief, while NMES units are used for muscle rehabilitation and strengthening. IFC devices use two sets of electrical currents to provide deeper stimulation to the muscles.
It’s important to note that EMS should be used under the guidance of a trained healthcare professional, as incorrect use can lead to injury or other complications. EMS is not appropriate for everyone, including people with pacemakers or other implanted medical devices, pregnant women, and individuals with certain medical conditions.
In summary, electro stim muscles is a technique that uses electrical impulses to stimulate muscle contractions. It has a wide range of applications in physical therapy, sports medicine, and fitness, and can be used for rehabilitation, muscle strength and endurance, pain relief, and athletic performance. If you are considering using EMS, it is important to consult with a healthcare professional to determine if it is safe and appropriate for your individual needs.
Does Electronic Muscle Stimulation Work?
There is evidence to suggest that electronic muscle stimulation (EMS) can be effective for certain purposes. For example, EMS has been shown to be effective in improving muscle strength and function in people undergoing rehabilitation after injury or surgery. It can also be effective in reducing pain and inflammation.
When used in conjunction with traditional resistance training, EMS has been shown to enhance muscle growth and strength in healthy individuals. However, it is important to note that EMS should not be used as a substitute for regular exercise.
While EMS can be effective, it is not appropriate for everyone. Individuals with certain medical conditions or implanted medical devices may be at risk of complications from EMS. Additionally, improper use of EMS can lead to injury or other complications. It is important to consult with a healthcare professional before using EMS to determine if it is safe and appropriate for your individual needs.
How Does a Muscle Stimulator Machine Work?
A muscle stimulator machine, also known as an electrical muscle stimulator (EMS) or neuromuscular electrical stimulation (NMES) device, works by delivering electrical impulses to muscles through electrodes placed on the skin. The electrical impulses cause the muscles to contract and relax, simulating the natural contraction and relaxation of muscles during exercise.
The machine typically has a control unit that generates the electrical impulses and electrodes that are placed on the skin over the muscles to be stimulated. The electrodes deliver the electrical impulses to the muscles, causing them to contract and relax.
The machine typically has adjustable settings for the intensity, frequency, and duration of the electrical impulses. The intensity refers to the strength of the electrical impulses, while the frequency refers to the number of electrical impulses delivered per second. The duration refers to the length of time that the electrical impulses are delivered.
Is Electrical Muscle Stimulation Safe?
Electrical muscle stimulation (EMS) is generally considered safe when used properly and under the guidance of a trained healthcare professional. However, as with any medical treatment or therapy, there are some potential risks associated with EMS.
One of the main risks is skin irritation or burns from the electrodes used to deliver the electrical impulses. This risk can be minimized by ensuring that the electrodes are placed correctly and that the appropriate level of intensity is used.
Another potential risk is muscle soreness or fatigue following EMS, particularly if the intensity or duration of the treatment is too high. It is important to start with low levels of intensity and gradually increase as tolerated.
Individuals with certain medical conditions or implanted medical devices may be at risk of complications from EMS. Pregnant women and individuals with epilepsy or a history of seizures should also avoid EMS.
It is important to note that EMS should not be used as a substitute for regular exercise. While EMS can be effective in improving muscle strength and function, it is not a replacement for traditional exercise. It is important to consult with a healthcare professional before using EMS to determine if it is safe and appropriate for your individual needs.
What Are The Side Effects Of Electric Muscle Stimulators?
While electrical muscle stimulators (EMS) are generally safe when used appropriately, there are potential side effects that should be considered. Some of the most common side effects of ems muscle stimulators include:
Skin irritation or burns from the electrodes used to deliver the electrical impulses. This can occur if the electrodes are not placed correctly or if the intensity is too high.Muscle soreness or fatigue following EMS, particularly if the intensity or duration of the treatment is too high. Tissue damage or injury, including muscle damage or nerve damage, if the device is not used properly or if the intensity is too high. Pain, discomfort, or cramping in the muscles during or after treatment. Headaches or dizziness, particularly if the treatment is used on the head or neck. Interference with implanted medical devices, such as pacemakers, which can cause serious complications.
It is important to note that these side effects are generally mild and temporary, and can often be avoided by using the device properly and under the guidance of a trained healthcare professional. Additionally, individuals with certain medical conditions or implanted medical devices should avoid using ems muscle stimulators, as they may be at higher risk of complications.
There are places that do this in Turkey and in Istanbul. It is important to note that the work should be done by experts.
